TESLA CARS
Tesla, Inc. (formerly Tesla Motors, Inc.) is an American automotive and energy company based in Palo Alto, California.[7] The company specializes in electric car manufacturing and, through its SolarCity subsidiary, solar panel manufacturing. It operates multiple production and assembly plants, notably Gigafactory 1[8] near Reno, Nevada, and its main vehicle manufacturing facility at Tesla Factory[9] in Fremont, California. As of March 2019, Tesla sells the Model S,[10] Model X,[11] and Model 3 automobiles.[12] It is accepting reservations for the Model Y,[13] Roadster (2020),[14] and Semi[15] vehicles. Tesla also sells Powerwall[16] and Powerpack[17] batteries, solar panels,[18] solar roof tiles,[19] and some related products.
Tesla was founded in July 2003, by engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, under the name Tesla Motors. The company’s name was derived from engineer Nikola Tesla. In early Series A funding, Tesla Motors was joined by Elon Musk, J. B. Straubel and Ian Wright, all of whom are retroactively allowed to call themselves co-founders of the company. Musk, who formerly served as chairman and is the current chief executive officer, said that he envisioned Tesla Motors as a technology company and independent automaker, aimed at eventually offering electric cars at prices affordable to the average consumer. Tesla Motors shortened its name to Tesla in February 2017.
As a vertically-integrated manufacturer, Tesla has had to master multiple technology domains, including batteries, electric motors, sensors, and artificial intelligence.
Batteries
Tesla Supercharger in West Hartford, Connecticut
Unlike other automakers, Tesla does not use individual large battery cells, but thousands of small, cylindrical, lithium-ion commodity cells like those used in consumer electronics. It uses a version of these cells that is designed to be cheaper to manufacture and lighter than standard cells by removing some safety features. According to Tesla, these features are redundant because of the advanced thermal management system and an intumescent chemical in the battery to prevent fires.[137] Panasonic is the sole supplier of the cells for Model S, Model X, and Model 3 and cooperates with Tesla in the Gigafactory 1’s ‘21–70‘ cells.[138]
In February 2016, Tesla battery cell costs were estimated at US$200 per kWh.[39] Tesla indicated later in 2016 that their battery cells cost less than $190/kWh.[139] Still later that year Argonne Labs estimated $163/kWh at a production rate of 500,000 packs per year.[140][141] In the 2018 Tesla Shareholder meeting, Elon Musk stated battery cell cost could be $100/kWh this year (2018). 2020 would bring $100/kWh Tesla battery packs (as opposed to battery cell).[142]
The batteries are placed under the vehicle floor. This saves interior and trunk space but increases risk of battery damage by debris or impact. The Model S has 0.25 in (6.4 mm) aluminum-alloy armor plate.[143] CTO Straubel expected batteries to last 10–15 years,[144] and discounts using electric cars to charge the grid (V2G) because the related battery wear outweighs economic benefit. He also prefers recycling over re-use for grid once they reach the end of their useful life for vehicles.[145][146] Since 2008, Tesla has worked with ToxCo/Kinsbursky to recycle worn out RoHS batteries, which will be an integral part of all Gigafactories.[147][148][149]
Motors
Tesla makes two kinds of electric motors. A three-phase four-pole AC induction motor with a copper rotor[150] (by which the Tesla logo is inspired) is used in the Model S and Model X, and permanent magnet motors are used in the Model 3 and Semi. Motors for the Model S and Model X are made at Tesla Factory, while motors for Model 3 are made at Gigafactory 1.
Autopilot
Tesla Autopilot provides semi-autonomous driver assist beginning in September 2014. Tesla replaced its sensors and software in 2016 (Hardware version 2, or “HW2”). As of 2017, Autopilot included adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, emergency braking, Autosteer (semi-automated steering), Autopark (parallel and perpendicular parking) and Summon (recalling the vehicle from a parking place).[151][152] HW2 includes eight cameras and twelve ultrasonic sensors, in addition to forward-facing radar.[153] HW2.5 was released in mid-2017 that upgraded HW2 with a second GPU and, for the Model 3 only, a driver-facing camera.[154]
At the end of 2016, Tesla expected to demonstrate full autonomy by the end of 2017,[155][156] which is now expected in 2019.[157] In April 2017 Musk predicted that in around two years drivers would be able to sleep in their vehicle while it drives itself.[158]
Glass
In November 2016, the company announced the Tesla glass technology group. The group produced the roof glass for the Tesla Model 3 and for use in SolarCity roof tiles announced in October 2016.[159] The tiles contain an embedded solar collector, and are one-third lighter than standard roof tiles.[160]
Vehicle models
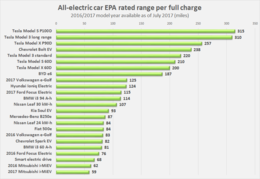
Comparison of EPA-rated range for model year 2016 and 2017 electric cars rated up until July 2017. Tesla vehicles shown correspond to the variants with the longest and shortest range for each model (S, X and 3).[161][162]
As of January 2019, Tesla offers three car models: the Model S, Model X and Model 3. The firm’s first vehicle, the first-generation Tesla Roadster is no longer sold.
Production
Model S
Model S deliveries began on June 22, 2012.[163] The first delivery in Europe took place in August 2013.[164] Deliveries in China began in April 2014.[165] First deliveries of the right-hand-drive model destined for the UK, Australia, Hong Kong and Japan came in 2014.[166] As of January 14, 2019, the Model S has three configurations: the Model S, the Model S Extended Range, and the Model S Performance with EPA ranges of 310 miles (500 km), 335 miles (539 km), and 315 miles (507 km) respectively.[167]
Norway is the Model S’ largest European market due to the country’s comprehensive incentives for the adoption of pure electric cars.
With an estimated 50,931 units sold in 2016, the Model S ranked as the world’s best-selling plug-in car for the second year in a row.[55][56] As of September 2018, the Model S, with global sales of 250,000 units, ranks as the world’s second best selling plug-in electric car in history after the Nissan Leaf (over 350,000 units).[88][89][91][168][169]
The United States is the world’s leading Model S market with an estimated 136,542 units sold through September 2018.[170] Norway ranked as the Model S largest overseas market as of November 2016,[171] with 11,802 new units registered.[172][173][174] The Tesla Model S became the first electric car ever to top the monthly sales ranking in any country, when the electric car achieved first place in the Norwegian new car sales list in September 2013.[175][176][177]
In May 2010 Tesla purchased a stake in what would become the Tesla Factory in Fremont, California, for US$42 million,[178][179][180] and opened the facility in October 2010.[179][181][182] For the European market, a final assembly plant and European Distribution Center are part of the Tesla facilities in Tilburg, Netherlands. Cars are built and tested in Fremont; then the battery pack, the electric motor and parts are disassembled and shipped separately to Tilburg, where they are reassembled.[183]
Among other awards, the Model S won the 2013 “Motor Trend Car of the Year“,[184] the 2013 “World Green Car“,[185] Automobile Magazine‘s 2013 “Car of the Year”,[186] and Time Magazine Best 25 Inventions of the Year 2012 award.[187]
Model X[edit]
Elon Musk delivering one of the first six Model X Founders Series models
The Tesla Model X is a mid-size crossover SUV with a lightweight aluminum body.[188] Model X deliveries started in September 2015.[189] It is offered in 5-, 6- and 7-passenger configurations. Notably, the passenger doors are articulating “falcon-wing” designs that open vertically.
Production was rescheduled several times, from 2013 to late 2014,[190] to the second quarter of 2015,[191] to the third quarter of 2015.[192] In August 2015, user groups estimated around 30,000 X pre-orders, compared to 12,000 for the S.[193]
Deliveries of the Model X Signature series began on September 29, 2015. Model X sales totaled 2,400 units during the first quarter of 2016, rising to 4,638 in the second quarter of 2016. Global deliveries totaled 25,312 units in 2016,[55] and 46,535 in 2017.[81][82][84][86][55]
In September 2016, the Model X ranked as the top selling plug-in electric car in Norway.[194][195] Previously, the Model S had been the top selling new car four times.[194] Cumulative sales since inception totaled 106,689 units through September 2018.[81][82][84][86][88][89][91][55] The United States is its main market with an estimated 57,327 units sold through September 2018.[170]
Model 3
Tesla Model 3 production model.
The Model 3 (originally stylized as “☰”) is Tesla’s third-generation car.[32] The car was originally intended to be called the Model E, but after a lawsuit from Ford that holds the trademark on “Model E”,[196] Musk announced on July 16, 2014 that the car would be called “Model 3” instead. The standard Model 3 is expected to deliver an EPA-rated all-electric range of 220 miles (350 km), while the long range model delivers 325 miles (523 km).[162]
On March 31, 2016, Tesla unveiled the car.[197] Potential customers began to reserve spots on March 31 with a refundable deposit.[198] Tens of thousands were reported waiting to reserve their spot.[199] As of April 7, 2016, one week after the unveiling, Tesla reported over 325,000 reservations,[200][201] representing sales of over US$14 billion.[202] As of July 2017, Tesla reported about 500,000 reservations.[203] Bloomberg News claimed “the Model 3’s unveiling was unique in the 100-year history of the mass-market automobile.” Bloomberg compared it to the 1955 Citroën DS that took in 80,000 deposits over 10-days at the Paris Auto Show.[204]
Tesla expected to invest between US$2 billion and US$2.5 billion in capital expenditures to support Model 3 production.[80] Limited vehicle production began in July 2017.[80] The first 30 units were delivered at a special event on July 28, 2017.[162] Customer deliveries totaled 1,764 units in the U.S. in 2017.[85][87] In June 2018 production reached 5,000 per week.[205] In January 2019, Tesla announced it would cut its full-time workforce by 7% – equal to about 3,150 employees – in order to reduce the cost of the Model 3 from $44,000 to $35,000.[206] Musk explained that while the company had “made great progress, our products are still too expensive for most people … There isn’t any other way.”[207]
The Model 3 topped plug-in electric car sales in the U.S. in 2018, with an estimated all-time record of 139,782 units delivered, after being the top-selling plug-in car in the country for 12 consecutive months since January 2018,[208][209] and marking the first time a plug-in car sold more than 100,000 units in a single year.[210] In addition, listed as the best selling plug-in car in California in 2018 with 51,293 units.[211][212] The Tesla Model 3 also topped global sales of plug-in electric passenger cars in 2018 with 146,055 units delivered.[20] Global sales since inception totaled 198,719 units through March 2019.[85][87][93][94][95]
On February 28, 2019, Tesla announced that they would begin to roll out the Standard Range base model starting at $35,000.[213][214] In January 2019, the Model 3 passed the Model S to become the top selling all-electric car in the U.S. ever,[215] and, the next month, also passed the Chevrolet Volt to become the all-time best-selling plug-in electric car in the U.S.[216] Since inception, about 164,000 Model 3 cars have been delivered in the U.S. through March 2019.[217]
The Tesla Model 3 comes in 3 trims of the car. Standard Range Plus RWD, Dual Motor AWD Long Range and Performance models.
Unveiled
2020 Roadster
Through a surprise reveal at the end of the event that introduced the Semi on November 16, 2017, Tesla unveiled the 2020 Roadster. Musk said that the new model will have a range of 620 miles (1,000 km) on the 200 kWh battery pack and will achieve 0–60 mph in 1.9 seconds; it also will achieve 0–100 mph in 4.2 seconds,[218] and the top speed will be over 250 mph (400 km/h). The vehicle will have three electric motors allowing for all-wheel drive, and torque vectoring during cornering.[219]
At the time, the base price was set at US$200,000 while the first 1,000 units, the Founder’s series, would sell for US$250,000.[219] Reservations required a deposit of US$50,000, and those who ordered the Founder’s series paid the US$250,000 in full upon ordering. Those who made a reservation at the event were allowed a test drive with a driver in the prototype.[220]
Tesla Semi
The Tesla Semi is an all-electric Class 8 semi-trailer truck first mentioned in the 2016 Tesla Master plan.[221] Production is expected to begin in 2019.
The vehicle’s official announcement was at a November 16, 2017 press conference where two prototypes were shown. Musk confirmed that the range would be 500 miles (800 km) and that the zero to 60 mph time would be 5 seconds versus 15 seconds for a similar truck with a diesel engine.[222] The Semi will be powered by four electric motors of the type used in the Tesla Model 3 and will include an extensive set of hardware sensors to enable it to stay in its own lane, a safe distance away from other vehicles, and later, when software and regulatory conditions allow, provide self-driving car operation on highways.[223] Musk also announced that the company would be involved in installing a solar-powered global network of the Tesla Megacharger devices to make the Semi more attractive to potential long-haul customers. A 30-minute charge would provide 400 miles (640 km) of range.[224][225]
Model Y
In August 2013, Tesla trademarked the name “Model Y”.[226] In October 2015, Musk described a future “Model Y”.[227] In August 2017, Tesla announced that the Model Y would use the Model 3 platform.[228]
In February 2018, Tesla announced that they would unveil Model Y production plans within the next 3–6 months[229] and posted open positions for Model Y production and design. In May 2018, Musk said that the Model Y will be built on a platform that shares many components with the Model 3, and that the Model Y will be in production at the earliest in early 2020.[230] In July 2018, Musk rescheduled the Model Y unveiling to be March 2019.[231] In March 2019, Musk tweeted, “Model Y unveil event on March 14 at LA Design Studio”[232] also adding that “the Model Y would be 10% bigger than the Model 3 so would cost 10% more”.[233]
The Model Y unveiling occurred on March 14, 2019.[234] The car will have up to three rows of seats (up to 7 people) and will have a range of up to 300 miles (480 km).[234]
Other concepts
In 2016, Musk indicated he hoped to one day produce a car cheaper than the Model 3:[235][236]
There will be future cars that will be even more affordable down the road . . . With fourth generation and smaller cars and what not, we’ll ultimately be in a position where everyone can afford the car.
— Elon Musk at the Future Transport Solutions conference in Oslo, April 21, 2016
Musk wanted the first three models to spell “SEX”, but Ford owns the trademark to “Model E”,[237] so settled for “S3XY” by making the Model Y.[238]
On July 20, 2016, Musk detailed his new master plan for Tesla. It includes more affordable cars produced in higher volume, solar-power roofs, mid-size vehicles, SUVs and pickup trucks, as well as the refinement of autonomous vehicles and the creation of a sharing economy, in which cars can be active while the owner is not using them.[239] Tesla intends to build a minibus on the Model X platform.[240] In May 2017, Musk indicated that he might favor a 10-12 passenger version of the Model X over a dedicated minibus design.[241]
At the company’s annual shareholder meeting in June 2018, Musk revealed Tesla’s intention to enter a new market segment, offering a compact hatchback in “less than five years”.[242][243] He provided no details, and dodged a question about also producing a subcompact. Musk also put to rest hopes for a Tesla motorcycle, saying “we’re not going to do motorcycles”.[244]
In April 2019 Elon Musk announced Tesla is going to launch an unmanned taxi by the end of 2020. The company plans to have more than 1 million unmanned vehicles by this time.[245]